Why Winter is the Best Time for a Hearing Health Checkup
Winter has a way of slowing things down and giving you a chance to take
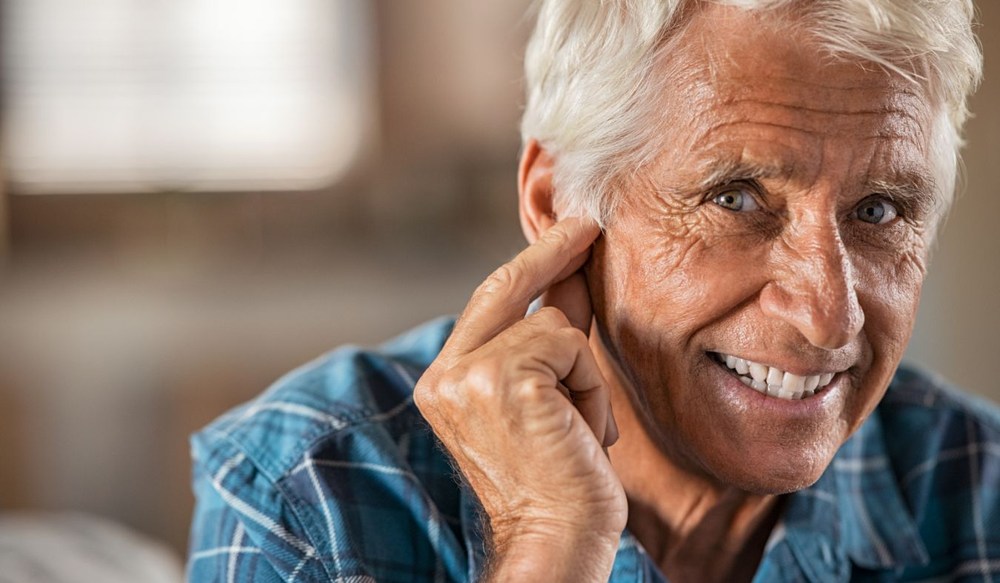


Winter has a way of slowing things down and giving you a chance to take
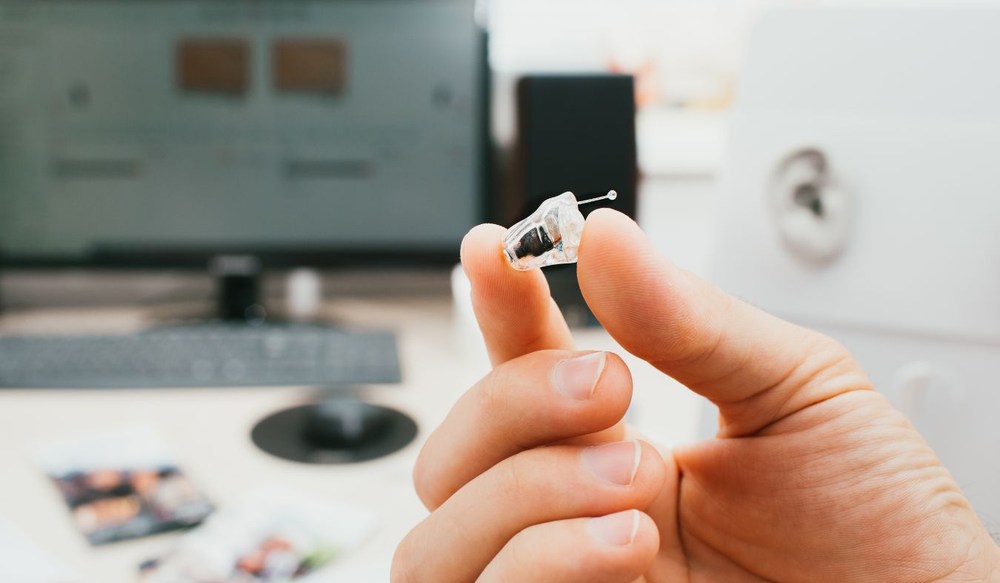

Hearing aid technology has come a long way in the past few years, and 2025
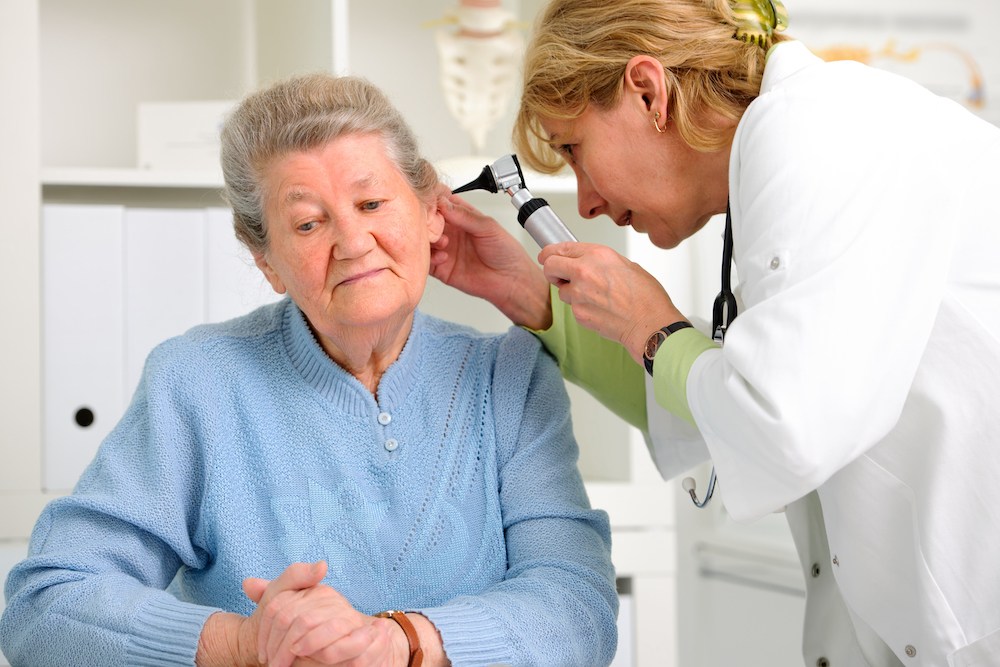
Hearing loss can subtly change daily life, influencing conversations with